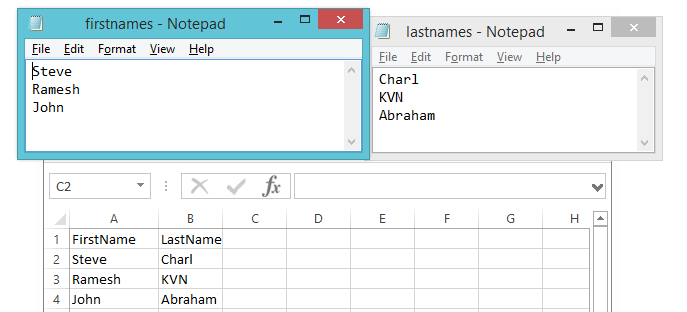
This post will discuss about querying DNS Server (Microsoft or Non-Microsoft) using PowerShell for different types of records like A, PTR, MX, NS, and resource records.
Nslookup.exe is a great utility for querying DNS servers. You can connect to server and query records types that you need. Its very useful utility but only problem is it is not flexible to use inside your scripts/automations. If this utility is used inside script, you to parse the text output to extract the details you need. Ideally anything that returns results in object format is very good in programming.
Are you looking for a script to resolve host name to IP and IP to host name using PowerShell, then check this post.
Alternative to nslookup in windows world is querying DNS server using WMI. There are WMI Classes available to query DNS server for various record types. Try below command to get a list of WMI classes that helps you to query and manage DNS running on a Windows Server.
Get-WmiObject -Namespace root\MicrosoftDNS -List
The downside with approach is, it works only for querying windows based DNS servers and this approach absolutely not valid for non Microsoft DNS server like bind. You can read about using these WMI classes using PowerShell at this Hey Scripting Guy post.
This problem is addressed in much better way in Windows 8/Windows Server 2012 with the introduction of Resolve-DNSName cmdlet. Using this cmdlet you can query any kind of DNS server(Microsoft or non-MS) for any record type without requiring any extra privileges and utilities. This cmdlet returns results in object format which is easy to consume within the script.
This cmdlet is part of DNSClient module in Windows 8/Windows Server 2012 or above Operating Systems. You cannot use this module on Windows 7 or any other previous operating systems.
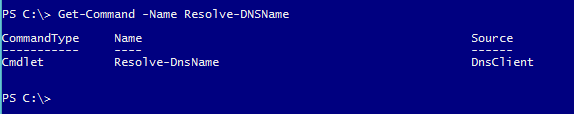
Now let us look at some examples to understand how to query DNS server using this.
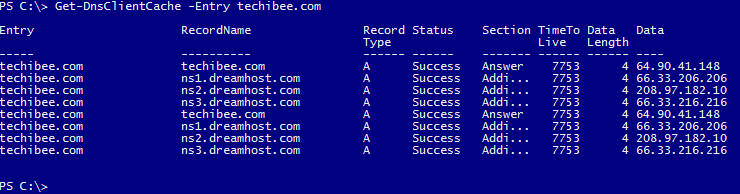
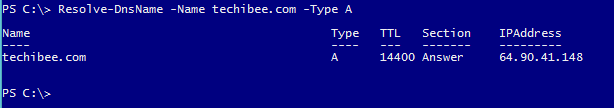
We can query A record techibee.com using below command. This queries the DNS servers that are listed in your network connection configuration. You can get DNS Server IP details of a computer using the script provided in this post.
Resolve-DnsName -Name techibee.com -Type A
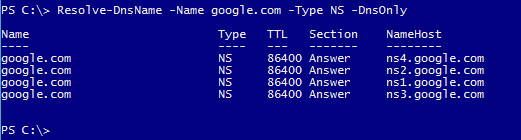
 Similarly you can query Name server rescords(NS) of a Domain by passing NS as value to -Type Parameter. This lists all name servers that are hosting the Domain name you are querying. Below examples shows how to query NS records of Google.com
Similarly you can query Name server rescords(NS) of a Domain by passing NS as value to -Type Parameter. This lists all name servers that are hosting the Domain name you are querying. Below examples shows how to query NS records of Google.com
Resolve-DnsName -Name google.com -Type NS -DnsOnly
We can target these queries against any DNS server in your network. For example, we can query Google name servers directly for a record or internal DNS server for records. Below command shows how to query a DNS server directly instead of relying on what is configured in local computer network configuration.
Resolve-DnsName -Name techibee.com -Type A -Server 202.156.1.16
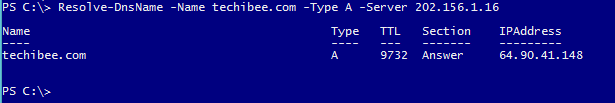
In above example, 202.156.1.16 is the IP of Google DNS server. You can try giving your internal DNS server name/IP or any external DNS name. It works same way as NSLookup does.
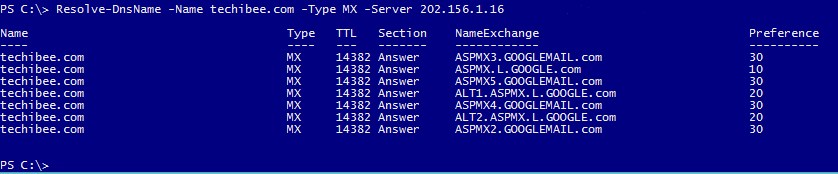
Similarly you can query MX records of a domain using below command.
Resolve-DnsName -Name techibee.com -Type MX -Server 202.156.1.16
You might be wondering what all types of records you can query using this cmdlet. Below is the list of records that this cmdlet supports.
If you have any questions about using this cmdlet, please write it in comments section.
Source : TechNet
| Record Name |
| A_AAAA |
| A |
| AAAA |
| NS |
| MX |
| MD |
| MF |
| CNAME |
| SOA |
| MB |
| MG |
| MR |
| NULL |
| WKS |
| PTR |
| HINFO |
| MINFO |
| TXT |
| RP |
| AFSDB |
| X25 |
| ISDN |
| RT |
| SRV |
| DNAME |
| OPT |
| DS |
| RRSIG |
| NSEC |
| DNSKEY |
| DHCID |
| NSEC3 |
| NSEC3PARAM |
| ANY |
| ALL |
Hope this helps….